How do LED Bulbs Work
LEDs became so popular these days, and many car owners replace regular halogen bulbs in their vehicles with LEDs. And we are talking not only about LED headlight conversion kits. Every vehicle features dozens of other accessory bulbs in both interior and exterior. Just knowing the bulb sizes for these bulbs, you can pick an LED replacement for each and every halogen bulb in your vehicle. No wonder LEDs became that popular these days, as they have got certain benefits over regular halogen bulbs.
Benefits of LED bulbs over halogen bulbs:
- Durability;
- Brightness;
- Low power consumption;
- Low resistance;
- Small size.
LED bulbs: Basic Terms
LED bulbs operate unlike regular incandescent bulbs, so here are some things tyou need to know about the way they work.
- CONDUCTORS: materials which electricity easily flows through:
✔ metal (esp. copper) is a great conductor of electricity;
✔ paper, plastic, wood are poor conductors of electricity.
- CURRENT: electrical “flow” (measured in amperes or amps).
- RESISTANCE: containment or resistance to flow (measured in ohms).
- VOLTAGE / VOLTS: electrical “pressure” or potential.
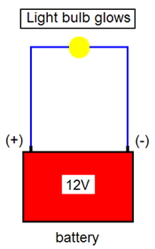
Electric flow must be a complete circuit for a device to work. Electrons always move from the negative side, where they are stored in excess, to the positive side, where they are attracted to the protons.
Description of electric flow
- Flow starts at battery negative (ground);
- Flow moves into and through device;
- Flow continues back to the battery positive (hot);
- Only when the flow is complete from battery negative to battery positive does the device work.
